Leaked internal Facebook documents show that a combination of technical miscommunications and high-level decisions led to one of the social media giant’s biggest broken promises of the 2020 election—that it would stop recommending political groups to users.
The Markup first revealed on Jan. 19 that Facebook was continuing to recommend political groups—including some in which users advocated violence and storming the U.S. Capitol—in spite of multiple promises not to do so, including one made under oath to Congress.
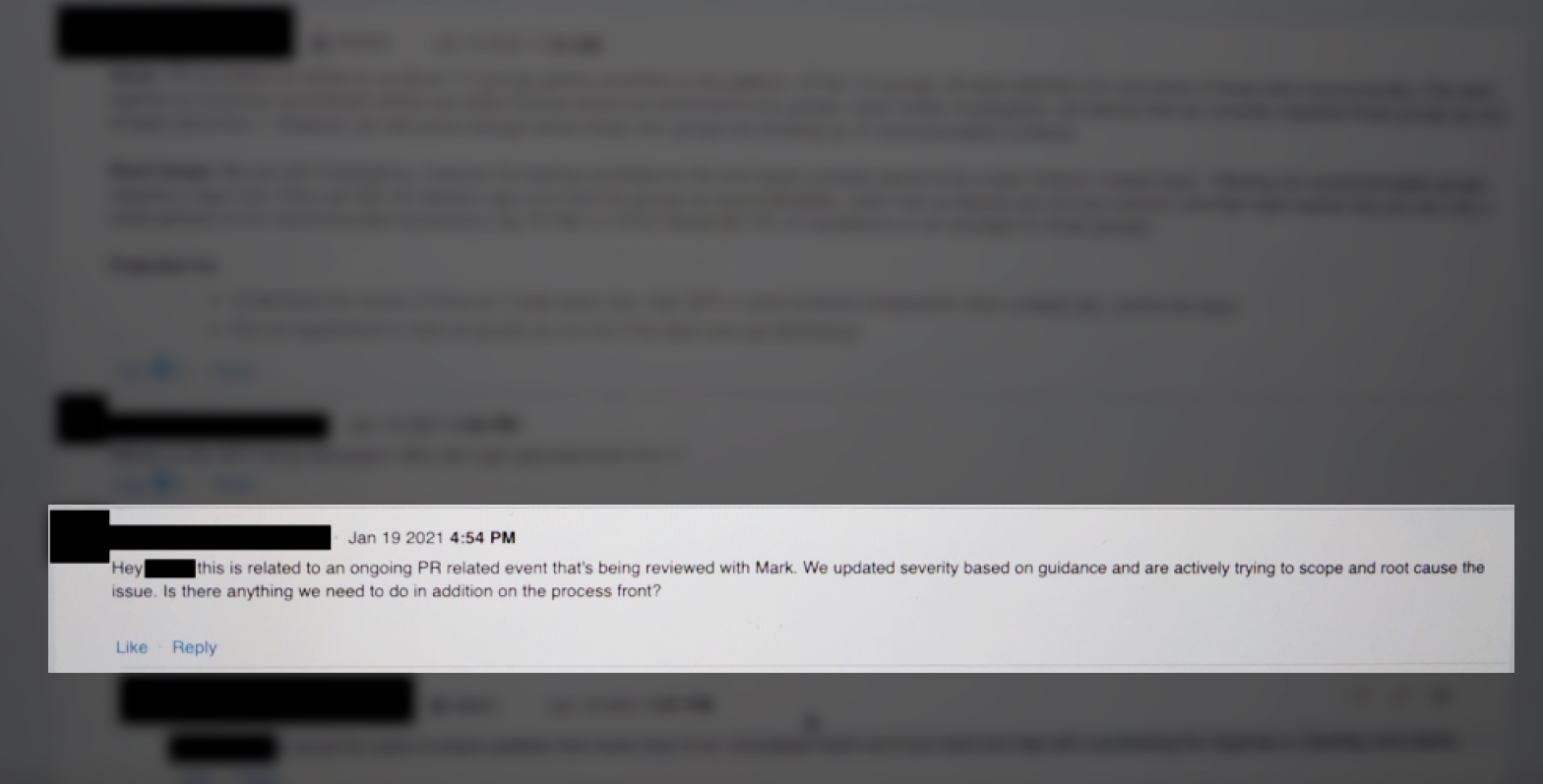
The day the article ran, a Facebook team started investigating the “leakage,” according to documents provided by Frances Haugen to Congress and shared with The Markup, and the problem was escalated to the highest level to be “reviewed by Mark.” Over the course of the next week, Facebook employees identified several causes for the broken promise.
The company, according to work log entries in the leaked documents, was updating its list of designated political groups, which it refers to as civic groups, in real time. But the systems that recommend groups to users were cached on servers and users’ devices and only updated every 24 to 48 hours in some cases. The lag resulted in users receiving recommendations for groups that had recently been designated political, according to the logs.
That technical oversight was compounded by a decision Facebook officials made about how to determine whether or not a particular group was political in nature.
When The Markup examined group recommendations using data from our Citizen Browser project—a paid, nationwide panel of Facebook users who automatically supply us data from their Facebook feeds—we designated groups as political or not based on their names, about pages, rules, and posted content. We found 12 political groups among the top 100 groups most frequently recommended to our panelists.
Facebook chose to define groups as political in a different way—by looking at the last seven days’ worth of content in a given group.
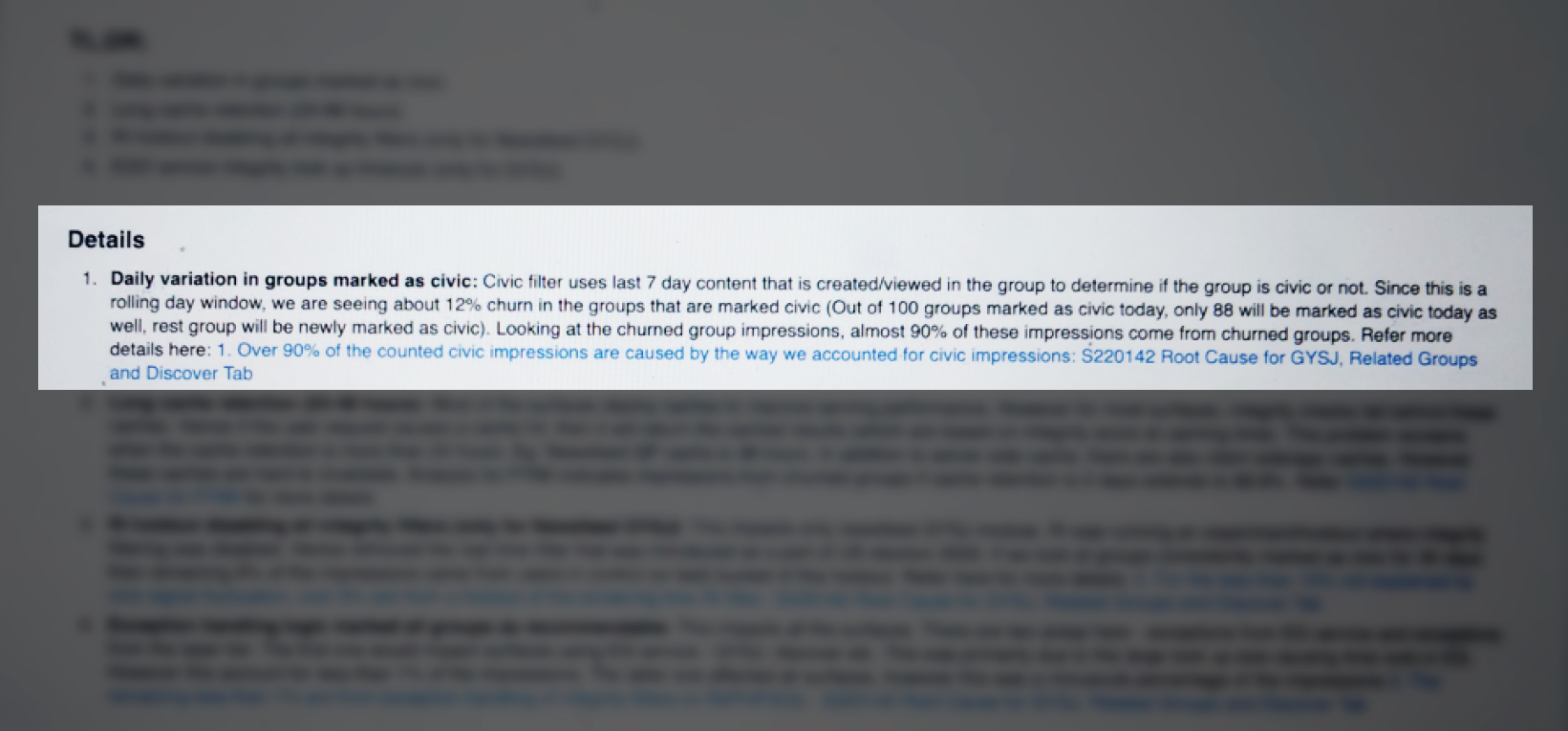
“Civic filter uses last 7 day content that is created/viewed in the group to determine if the group is civic or not,” according to a summary of the problem written by a Facebook employee working to solve the issue.
As a result, the company was seeing a “12% churn” in its list of groups designated as political. If a group went seven days without posting content the company’s algorithms deemed political, it would be taken off the blacklist and could once again be recommended to users.
Almost 90 percent of the impressions—the number of times a recommendation was seen—on political groups that Facebook tallied while trying to solve the recommendation problem were a result of the day-to-day turnover on the civic group blacklist, according to the documents.
Facebook did not directly respond to questions for this story.
“We learned that some civic groups were recommended to users, and we looked into it,” Facebook spokesperson Leonard Lam wrote in an email to The Markup. “The issue stemmed from the filtering process after designation that allowed some Groups to remain in the recommendation pool and be visible to a small number of people when they should not have been. Since becoming aware of the issue, we worked quickly to update our processes, and we continue this work to improve our designation and filtering processes to make them as accurate and effective as possible.”
Social networking and misinformation researchers say that the company’s decision to classify groups as political based on seven days’ worth of content was always likely to fall short.
“They’re definitely going to be missing signals with that because groups are extremely dynamic,” said Jane Lytvynenko, a research fellow at the Harvard Shorenstein Center’s Technology and Social Change Project. “Looking at the last seven days, rather than groups as a whole and the stated intent of groups, is going to give you different results. It seems like maybe what they were trying to do is not cast too wide of a net with political groups.”
Many of the groups Facebook recommended to Citizen Browser users had overtly political names.
More than 19 percent of Citizen Browser panelists who voted for Donald Trump received recommendations for a group called Candace Owens for POTUS, 2024, for example. While Joe Biden voters were less likely to be nudged toward political groups, some received recommendations for groups like Lincoln Project Americans Protecting Democracy.

Citizen Browser
Facebook Said It Would Stop Pushing Users to Join Partisan Political Groups. It Didn’t
According to Citizen Browser data, the platform especially peppered Trump voters with political group recommendations
The internal Facebook investigation into the political recommendations confirmed these problems. By Jan. 25, six days after The Markup’s original article, a Facebook employee declared that the problem was “mitigated,” although root causes were still under investigation.
On Feb. 10, Facebook blamed the problem on “technical issues” in a letter it sent to U.S. senator Ed Markey, who had demanded an explanation.
In the early days after the company’s internal investigation, the issue appeared to have been resolved. Both Citizen Browser and Facebook’s internal data showed that recommendations for political groups had virtually disappeared.
But when The Markup reexamined Facebook’s recommendations in June, we discovered that the platform was once again nudging Citizen Browser users toward political groups, including some in which members explicitly advocated violence.
From February to June, just under one-third of Citizen Browser’s 2,315 panelists received recommendations to join a political group. That included groups with names like Progressive Democrats of Nevada, Michigan Republicans, Liberty lovers for Ted Cruz, and Bernie Sanders for President, 2020.